Calculating and managing direct labor efficiency variance is essential for controlling labor costs in the construction industry. We’ll also show the formula used to calculate it and the factors my fuel tax that affect its calculation. By the end, you’ll be able to understand how this measurement can improve your project’s labor costs, which means that it will ensure a more profitable outcome.
Explanation of Direct Labor Variance
At the end of the day, your business will grow only if you can get the most out of your workforce and minimize waste at the same time. With the right tools and practices, achieving optimal labor efficiency is not just possible; it is something that will arrive sooner or later. High productivity means workers complete tasks more quickly, potentially leading to favorable efficiency variances. Conversely, low productivity can result in unfavorable variances due to more hours worked than expected. Possible causes of an unfavorable efficiency variance include poorly trained workers, poor quality materials, faulty equipment, and poor supervision.
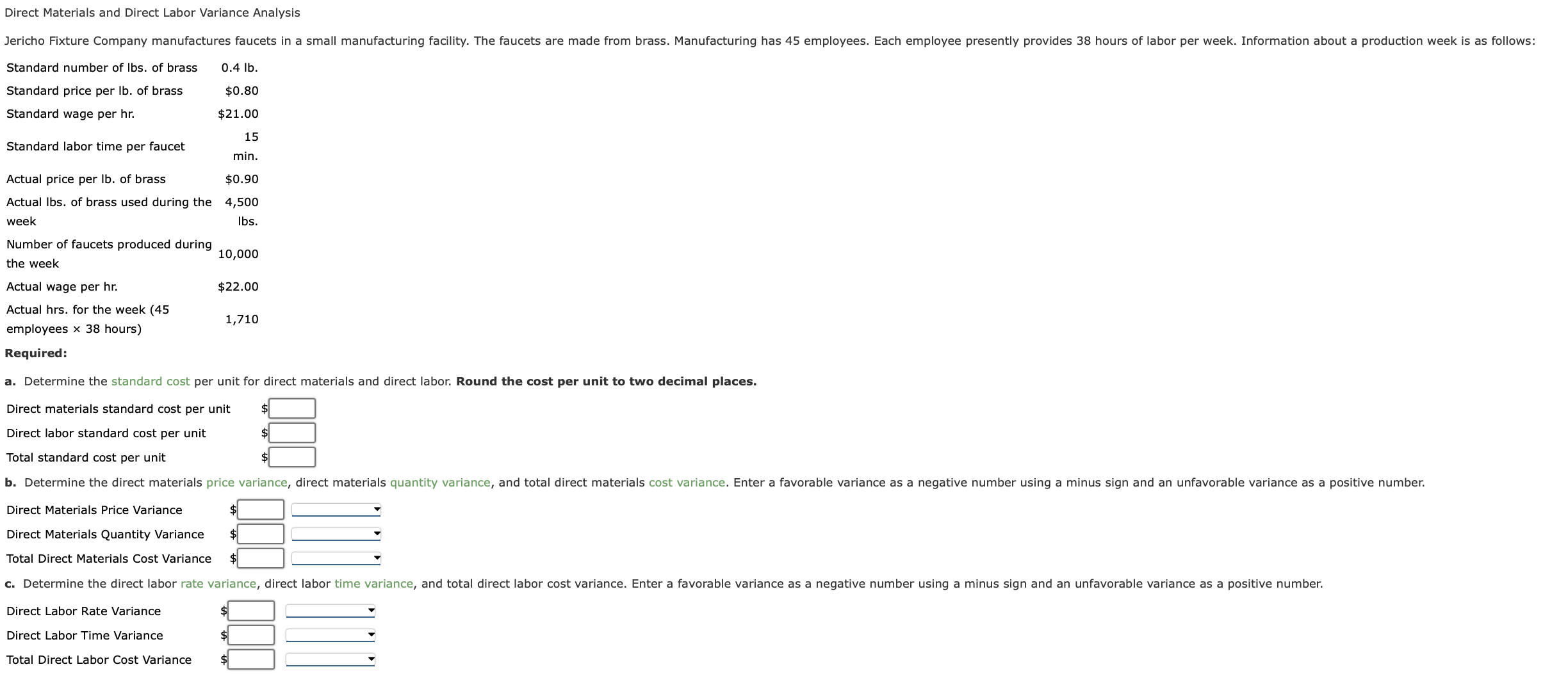
3: Direct Labor Cost Variance
- A direct labor cost variance occurs when a company pays a higher or lower price than the standard price set.
- It is very important to measure how close you are to what you expected in order to determine how well labor is utilized on a jobsite.
- The combination of the two variances can produce one overall total direct labor cost variance.
- For proper financial measurement, the variance is normally expressed in dollars rather than hours.
- Shortages or poor-quality tools can hinder productivity, causing unfavorable variances.
It measures the difference between the actual labor costs incurred during production and the standard labor costs that were expected or budgeted. This variance can provide valuable insights into how well a company is managing its workforce and whether labor costs are being controlled effectively. Direct labor efficiency variance is a financial metric that takes the standard labor hours estimated during the planning phase of a project and compares them with the actual direct labor hours that have been used.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
Kenneth W. Boyd has 30 years of experience in accounting and financial services. He is a four-time Dummies book author, a blogger, and a video host on accounting and finance topics. Average acceleration is the object’s change in speed for a specific given time period. The more Direct Labor Mix Variance is decreased, the less wasted resources are on production, and the better chance there is that products will be produced within their optimal amount of time. With real-time visibility, construction managers can make data-driven decisions that reduce labor inefficiencies and improve project timelines.
Computing Direct Labor Variance
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University.
This variance helps businesses understand whether their workforce is working more or fewer hours than expected to produce a given level of output. If the total actual cost is higher than the total standard cost, the variance is unfavorable since the company paid more than what it expected to pay. By applying these lessons, companies can better manage their labor costs, improve productivity, and achieve greater financial control and stability. These case studies highlight the importance of regular variance analysis and proactive management in addressing labor-related challenges.
It gives you accurate data on direct labor hours, so you’ll be able to quickly identify inefficiencies and eradicate them before they impact the project’s budget. Several factors can impact your direct labor efficiency variance on the construction site. Understanding these can help you identify potential issues and implement corrective actions. Before we take a look at the direct labor efficiency variance, let’s check your understanding of the cost variance. Working conditions and employee morale play a significant role in labor efficiency.
Labor mix variance is the difference between the actual mix of labor and standard mix, caused by hiring or training costs. Direct Labor Yield Variance (DLYV) is a measure of the difference between actual and expected labor costs, based on the number of units produced or services provided. If the total actual cost incurred is less than the total standard cost, the variance is favorable. Direct Labor Mix Variance can be used to make a product more cost-efficient, less wasteful of resources, and save time during production. It is used to increase the profits of the company by saving money on labor costs.
SmartBarrel makes 100% accurate time tracking stupid simple — saving you hours every week, keeping your job costs on track, and eliminating all payroll disputes. Direct Labor Mix Variance is typically calculated by subtracting the actual amount of labor used from the budgeted amount, then dividing the result by the budgeted amount. Direct Labor Mix Variance typically occurs when the actual labor mix used in production is different from what was budgeted or anticipated.
Like direct labor rate variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. On the other hand, if workers take an amount of time that is more than the amount of time allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance. They provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of a company’s labor cost control and workforce utilization. By regularly analyzing labor variances, companies can identify discrepancies between actual and budgeted costs, understand the root causes of these variances, and take corrective actions. This proactive approach not only helps in managing labor costs more effectively but also contributes to better budgeting, forecasting, and strategic decision-making.